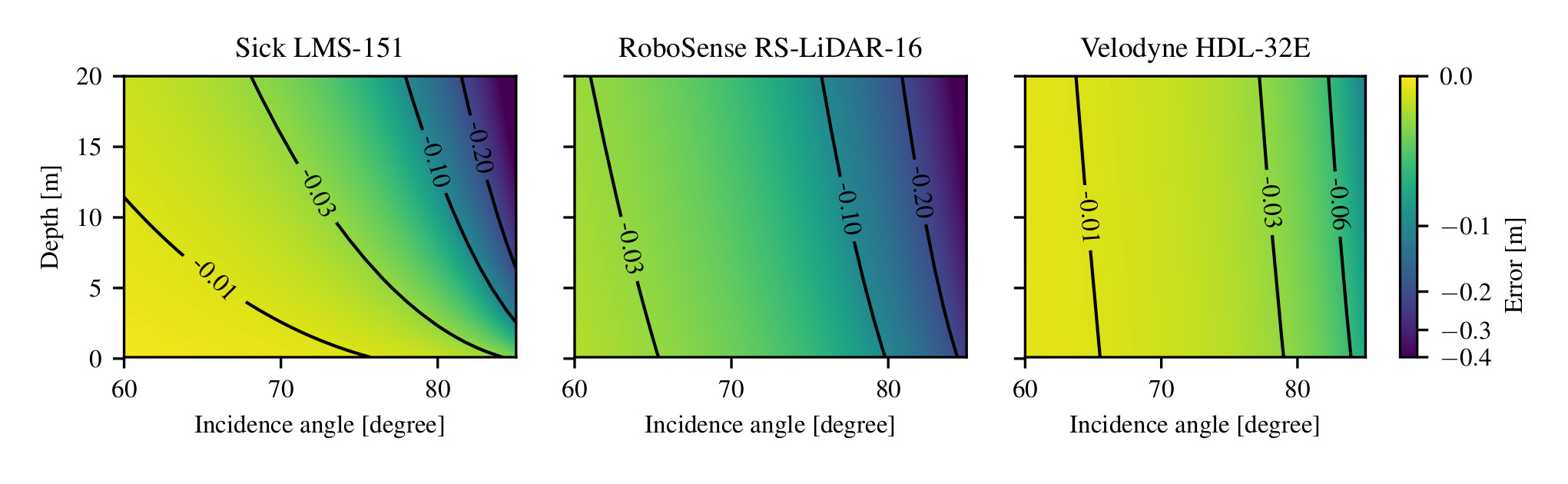
In a context of 3D mapping, it is very important to obtain accurate measurements from sensors. In particular, LIDAR measurements are typically treated as a zero-mean Gaussian distribution. We show that this assumption leads to predictable localisation drifts, especially when a bias related to measuring obstacles with high incidence angles is not taken into consideration. Moreover, we present a way to physically understand and model this bias, which generalizes to multiple sensors. Using an experimental setup, we measured the bias of the Sick LMS-151, Velodyne HDL-32E, and Robosense RS-LiDAR-16 as a function of depth and incidence angle, and showed that the bias can reach 20 cm for high incidence angles. We then used our model to remove the bias from the measurements, leading to more accurate maps and a reduced localisation drift.
Contributions
- Physical explanation of a lidar bias caused by the incidence angle of the laser beam on a surface
- A way to quantify and correct this bias for common LIDARs used in mobile robotics
Results in Images
Using our model, we found the following bias for three commonly used LIDARs:
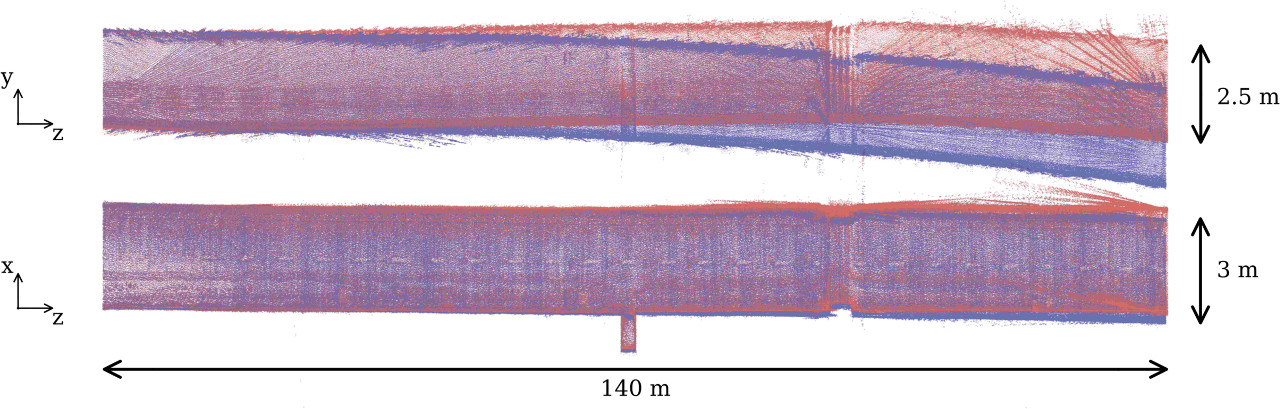
We were able to remove the bias from the measurements, leading to more accurate maps.
In blue, the map of a tunnel without taking into account the bias.
In red, the same map taking into account the bias and removing it from the measurements.
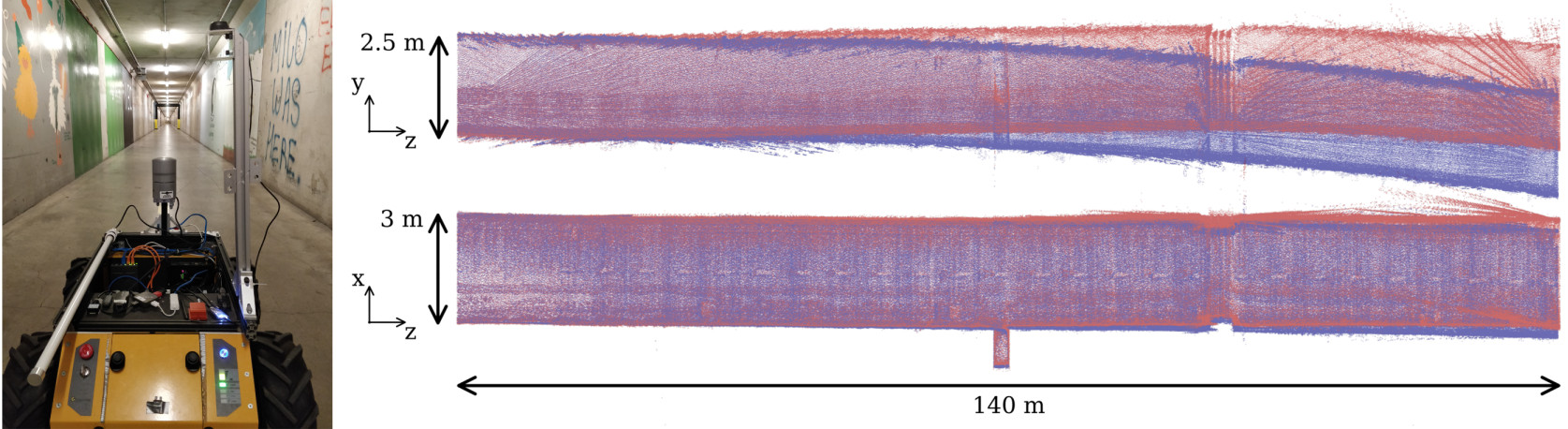
In Video
Reference
Laconte, J., Deschênes, S.-P., Labussière, M., & Pomerleau, F. (2019). Lidar Measurement Bias Estimation via Return Waveform Modelling in a Context of 3D Mapping. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).